Product Description
Product Variety:
Total coupling, Harf coupling, Minimizing coupling, Reducer insert, Union, 90°elbow, 45°elbow,
Tee, Cross, Cap, Cross, Square head plug, Hex head plug, Round head plug, Hex head bushing,
Union, Minimizing swage, Welding Boss, Mitre Boss, High Stress Boss, Socket Lowering Insert.
Size:
1/2″ to 4″(DN15~DN100)
Assortment(Wall Thickness):
3000LB to 9000LB
XS, Sch80, Sch160, XXS.
Common:
ASME/ANSI B16.eleven, MSS SP-seventy nine, MSS SP-83, MSS SP-ninety five, MSS SP-114, JIS B2316, JIS B2302 and so forth.
Materials:
Stainless metal, Duplex metal, Alloy metal, Carbon Metal, Reduced-temperature steel,
Nonferrous steel (Nickel Alloy, Aluminum Alloy , Titanium Alloy,…) and many others.
+ SOCKET WELD FITTINGS
A Socket Weld is a pipe attachment element in which a pipe is inserted into a recessed spot of a Valve, fitting or flange. In contrast to butt-weld fittings, Socket Weld fittings are mostly utilised for small pipe diameters (Small Bore Piping) typically for piping whose nominal diameter is NPS 2 or smaller sized.
To join pipe to Valves and fittings or to other sections of pipe, fillet-type seal welds be utilised. Socket-welded Joints construction is a excellent option where ever the positive aspects of high leakage integrity and great structural power are important design and style concerns.
Tiredness resistance is reduce than that in butt-welded construction due to the use of fillet welds and abrupt fitting geometry, but it is even now better than that of most mechanical becoming a member of techniques.
SW Fittings are family members of high pressure fittings are used in numerous industrial procedures.
Kinds of Threaded Fittings by Class and Dimensions
| Description | Course Designation |
||
| 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | |
| Elbows 45 and 90 degrees, Tees, Crosses, Couplings, Fifty percent-Couplings, Conclude or Pipe Caps |
one/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – two |
| one/2 – 4 | 1/2 – two | one/2 – 2 | |
| one/2 – 4 | one/2 – two | one/2 – two | |
| Pipe Dimensions by Wall Thickness |
SCH 80 / XS | SCH one hundred sixty | XXS |
Plugs and Bushings are not determined. They might be employed up via Course 6000 NPS
+THREADED FITTINGS
Threaded joints most likely signify the oldest strategy of becoming a member of piping systems. Like Socket Weld fittings, threaded fittings are mainly employed for modest pipe diameters (Small Bore Piping) normally for piping whose nominal diameter is NPS 2 or scaled-down.
Types of Threaded Fittings by Course and Dimension
| Description |
Class Designation |
||
| 2000 | 3000 | 6000 | |
| Elbows forty five and 90 levels Tees, Crosses, Coupling Half-Coupling, Cap |
one/2 – 4 | one/2 – 2 | one/2 – 2 |
| one/2 – four | 1/2 – 2 | one/2 – two | |
| 1/2 – four | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 | |
| Pipe Wall | SCH 80 / XS | SCH 160 | XXS |
Plugs and Bushings are not determined. They may possibly be employed up by means of Class 6000
|
US $1 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Wall Thickness: | All Thickness |
|---|---|
| Transport Package: | Wooden and Acc. to Customer′s Requirements. |
| Specification: | CE, ASME, API, AD2000, BV, ABS, ISO9001 |
| Trademark: | Chanyat |
| Origin: | China |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Description | Class Designation |
||
| 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | |
| Elbows 45 and 90 degrees, Tees, Crosses, Couplings, Half-Couplings, End or Pipe Caps |
1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 |
| 1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 | |
| 1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 | |
| Pipe Size by Wall Thickness |
SCH 80 / XS | SCH 160 | XXS |
###
| Description |
Class Designation
|
||
| 2000 | 3000 | 6000 | |
| Elbows 45 and 90 degrees Tees, Crosses, Coupling Half-Coupling, Cap |
1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 |
| 1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 | |
| 1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 | |
| Pipe Wall | SCH 80 / XS | SCH 160 | XXS |
|
US $1 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Wall Thickness: | All Thickness |
|---|---|
| Transport Package: | Wooden and Acc. to Customer′s Requirements. |
| Specification: | CE, ASME, API, AD2000, BV, ABS, ISO9001 |
| Trademark: | Chanyat |
| Origin: | China |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Description | Class Designation |
||
| 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | |
| Elbows 45 and 90 degrees, Tees, Crosses, Couplings, Half-Couplings, End or Pipe Caps |
1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 |
| 1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 | |
| 1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 | |
| Pipe Size by Wall Thickness |
SCH 80 / XS | SCH 160 | XXS |
###
| Description |
Class Designation
|
||
| 2000 | 3000 | 6000 | |
| Elbows 45 and 90 degrees Tees, Crosses, Coupling Half-Coupling, Cap |
1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 |
| 1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 | |
| 1/2 – 4 | 1/2 – 2 | 1/2 – 2 | |
| Pipe Wall | SCH 80 / XS | SCH 160 | XXS |
What Is a Coupling?
A coupling is a device that connects two shafts together. It transmits power from one to the other and is used to join rotating equipment. It can also allow for some degree of misalignment and end movement. It is used in mechanical engineering and manufacturing. To learn more about couplings, read this article. Mechanical connection between two objectsThe present invention relates to a method and assembly for forming a mechanical connection between two objects. The methods of this invention are suitable for connecting both solid and hollow objects. For example, the method can be used to make mechanical connections between two cylinders. This method is particularly useful for connecting two cylinders that are positioned near each other.
Mechanical connection between two objectsThe present invention relates to a method and assembly for forming a mechanical connection between two objects. The methods of this invention are suitable for connecting both solid and hollow objects. For example, the method can be used to make mechanical connections between two cylinders. This method is particularly useful for connecting two cylinders that are positioned near each other.
Absorbs vibration
A coupling insert is a part of a vehicle’s drivetrain that absorbs vibrations. These inserts are designed to prevent couplings from moving out of phase. However, the coupling inserts themselves can wear out and need to be replaced. Universal joints are an alternative if the coupling is out of phase by more than one degree. In addition, internal bearings in the coupling need to be lubricated and replaced when they begin to show signs of wear.
Another embodiment of the invention includes a flexible coupling 25 that includes rearwardly-extending lugs that extend toward the coupling member 23. These lugs interdigitate with corresponding lugs on the coupling member 23. They are spaced circumferentially. A first elastic member 28 is interposed between lugs 26 and 27, and is adapted to yield in a counterclockwise direction. As a result, it absorbs torsional vibrations.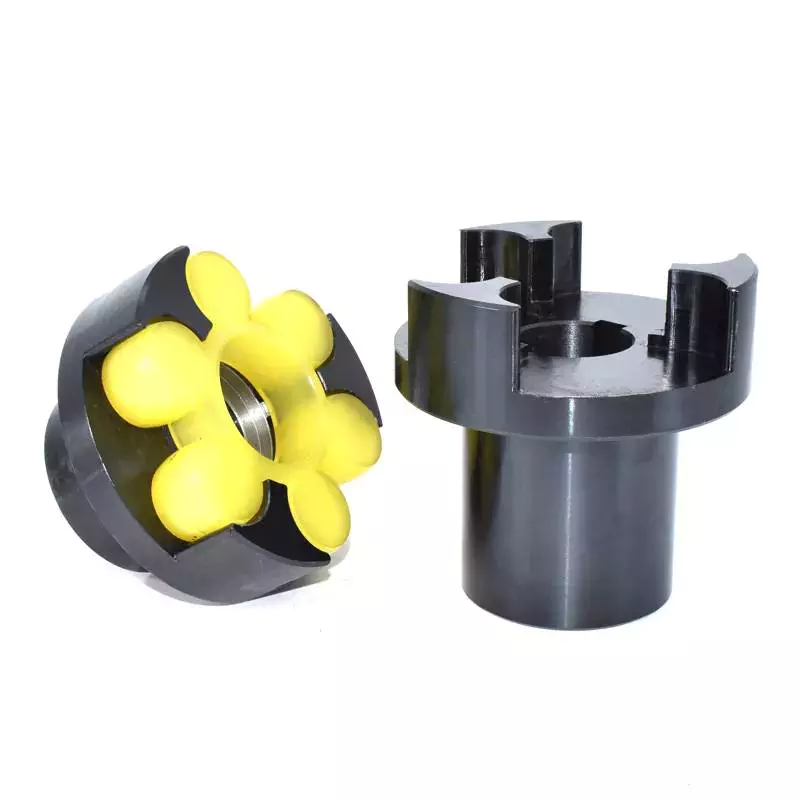
Blocks heat transfer
Thermal coupling occurs when a solid block is thermally coupled to the air or fluid passing through it. The amount of heat transferred through a solid block depends on the heat transfer coefficients of the materials. This paper presents a numerical model to understand how heat transfers through different block materials. This work also describes the thermal resistance network for a one-dimensional block.
In some cases, thermal coupling increases the heat transfer mechanism. As illustrated in FIG. 1D, a heatpipe coupler 112 couples two heatpipes 110-1 and 110-2. This configuration allows the pipes to be coupled to the heat source and to the condenser. In addition, the heat pipe couplers may have bellows at the ends to help facilitate linear motion.
Thermal coupling is achieved by ensuring that at least one block is made of a material with a lower thermal expansion coefficient than the annulus. Ideally, the block’s mean thermal expansion coefficient is at least twenty percent lower than the annulus’s mean thermal expansion coefficient. This ensures that the thermal coupling between the two parts is as efficient as possible.
Another type of thermal coupling is achieved by using flexible elements. These are often washers or springs. These components allow the blocks to maintain physical contact with the post 55, which means that the heat transfer is more efficient even at higher temperatures. The flexibility of these elements also makes it possible to choose an element that will not impede assembly.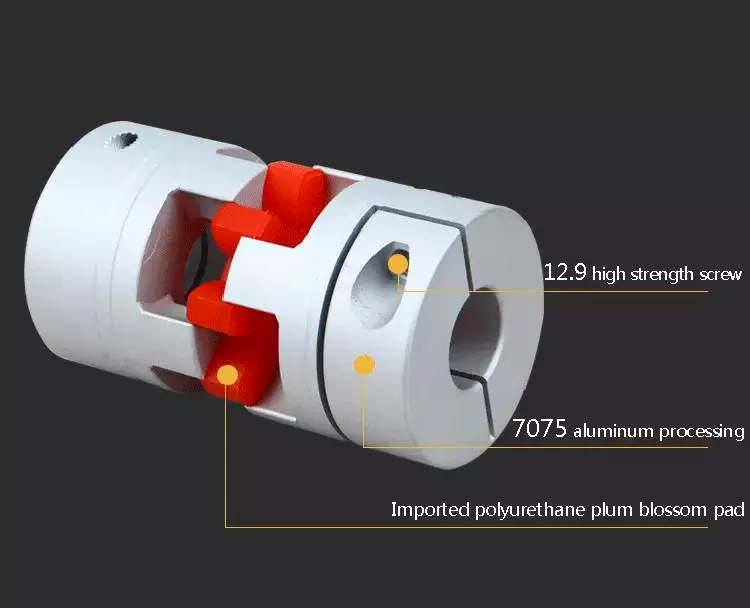
Protects rotating equipment
A reliable, long-lasting coupling system can reduce the risk of damage to rotating equipment. Designed to protect against torque overload and wear, Voith torque-limiting couplings provide outstanding safety and reliability. As a result, they can deliver maximum performance and minimize equipment downtime. In addition to their long-term benefits, these solutions are ideal for applications where safety and reliability are of paramount importance.
A good coupling provides many advantages, including the ability to transmit power, compensate for axial movement, and absorb shock. It is essential to choose the proper coupling for your application based on the basic conditions of your rotating equipment. For example, if you have two shafts with parallel rotation axes, you should choose a parallel coupling. Otherwise, you should use an angular coupling.
Torque-limiting couplings can also provide protection for rotating equipment by disengaging at a specific torque level. This protects the drive shaft from undergoing catastrophic failure. Torque limiters are particularly helpful for high-value equipment. By preventing catastrophic failure, you can avoid expensive repairs and minimize equipment downtime.
Coupling guards are easy to install and provide effective protection for rotating equipment. These covers are made of sheet metal bent to fit over the shaft. They are durable and easy to remove when necessary. This type of guard can prevent employees from catching their hands, tools, or loose clothing on motor coupling components.

editor by czh 2023-01-01